The Rise of the 43 Inch Monitor
The Demand for Larger Displays
As our reliance on digital technology continues to grow, the demand for larger and more immersive display solutions has been on the rise. The 43-inch monitor has emerged as a popular choice, offering a compelling balance between screen real estate and practical usability.
The Versatility of the 43-Inch Form Factor
The 43-inch monitor size caters to a wide range of applications, from professional workstations and gaming setups to home entertainment and digital signage. This versatility has made the 43-inch display a sought-after option for individuals and organizations seeking a display that can adapt to their diverse needs.
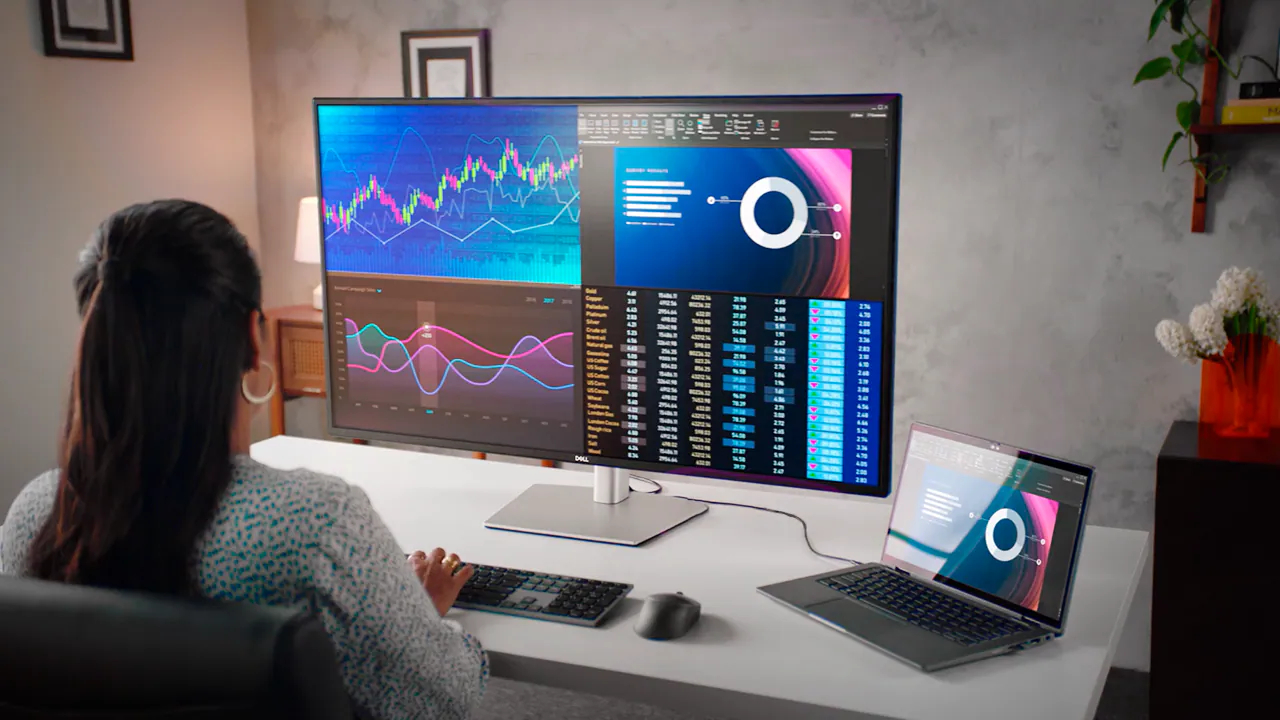
Key Features of the 43 Inch Monitor
43 inch monitor: Display Resolution and Clarity
One of the primary advantages of the 43-inch monitor is its ability to deliver high-resolution visuals. These displays often feature 4K (3840 x 2160) or even 5K (5120 x 2880) resolutions, providing users with stunning clarity, vivid colors, and exceptional detail.
43 inch monitor: Panel Technologies and Image Quality
The 43-inch monitors market showcases a variety of panel technologies, each with its own strengths. From IPS (In-Plane Switching) for exceptional color accuracy to VA (Vertical Alignment) for deep blacks and contrast ratios, users can choose the panel type that best suits their specific needs and preferences.
43 inch monitor: Connectivity and Integration
To ensure seamless integration with a wide range of devices, 43-inch monitors are typically equipped with a versatile array of connectivity options, including HDMI, DisplayPort, USB-C, and even wireless technologies like Bluetooth and Wi-Fi.

Choosing the Right 43 Inch Monitor
Determining the Intended Use Case
When selecting a 43-inch monitors, it’s crucial to consider the primary intended use case, whether it’s for productivity, gaming, multimedia consumption, or a combination of these. This will help guide the selection of features and specifications that best align with your needs.
Evaluating Display Performance
In addition to screen size, pay close attention to the monitor’s display performance metrics, such as refresh rate, response time, and color accuracy. These factors can have a significant impact on the overall user experience, particularly in demanding applications like gaming or professional content creation.
Assessing Ergonomic Features
The ergonomic design of a 43-inch monitors is also an important consideration, as it can contribute to user comfort and productivity. Look for features like adjustable stands, swivel and tilt capabilities, and the option for wall-mounting or VESA compatibility.

Utilizing the 43-Inch Monitor in Various Scenarios
Productivity and Multitasking
The expansive screen real estate of a 43-inch monitor can significantly enhance productivity and multitasking capabilities. Users can comfortably view multiple windows, applications, or documents side by side, improving their efficiency and workflow.
Gaming and Immersive Entertainment
For gaming enthusiasts and multimedia enthusiasts, the 43-inch monitor offers a more immersive and engaging experience. The larger screen size can provide a more cinematic feel, amplifying the visual and audio impact of games, movies, and other digital content.
Digital Signage and Presentation
The 43-inch monitor’s size and high-resolution capabilities make it an excellent choice for digital signage applications, such as information displays, advertising, and interactive presentations. The combination of visual impact and responsiveness can captivate audiences and convey information effectively.
Optimizing the 43-Inch Monitor Experience
Ergonomic Considerations
When using a 43-inch monitor, it’s essential to consider the ergonomic implications. Factors like viewing distance, eye level, and physical positioning can greatly impact the user’s comfort and overall experience. Proper ergonomic adjustments can help prevent eye strain, neck pain, and other physical discomorts.
Customizing the Display Settings
To get the most out of a 43-inch monitors, users should explore and customize the various display settings, such as brightness, contrast, color temperature, and image sharpness. These adjustments can help optimize the visual experience, whether for productivity, gaming, or multimedia consumption.

The Benefits of the 43-Inch Monitor
Enhanced Productivity and Efficiency
The expansive screen real estate of a monitors 43-inch can significantly boost productivity by allowing users to multitask more effectively, view larger amounts of content simultaneously, and minimize the need for constant window switching.
Immersive Viewing Experience
The large, high-resolution display of a monitors 43-inch can create a more immersive and engaging experience, particularly for activities like gaming, movie watching, and multimedia content consumption.
Improved Collaboration and Presentation
The impressive size and visual clarity of a monitors 43-inch make it an excellent choice for collaborative work environments, interactive presentations, and digital signage applications, where the display needs to be visible and engaging to a wider audience.
Considerations for Workspace Integration
Spatial Requirements and Placement
When integrating a monitor 43-inch into a workspace, it’s crucial to carefully consider the available space, desk size, and optimal viewing distance to ensure a comfortable and ergonomic setup.
Power and Connectivity Needs
Ensure that the workspace can accommodate the power requirements and connectivity options of the monitors 43-inch, including the necessary power outlets, HDMI or DisplayPort connections, and any additional USB or Ethernet ports.

The Future of 43-Inch Monitors
Advancements in Display Technology
As display technology continues to evolve, the monitors of 43 inch segment is poised to witness further advancements, such as the integration of higher refresh rates, improved color accuracy, and the adoption of cutting-edge panel technologies like OLED or Mini-LED.
Expanding Use Cases and Integrations
The versatility of the monitors 43-inch suggests that new and innovative use cases will continue to emerge, driven by evolving user needs, advancements in software and hardware, and the increasing integration of these displays with various technology ecosystems.
Conclusion
The 43-inch monitors has emerged as a versatile and powerful display solution, catering to a wide range of applications and user needs. Its large screen size, high-resolution capabilities, and diverse connectivity options make it an attractive choice for professionals, gamers, and multimedia enthusiasts alike. By carefully considering the intended use case, display performance, and ergonomic factors, users can unlock the full potential of the 43-inch monitor and enhance their digital experiences. As display technology continues to evolve, the 43-inch monitor is poised to play an even more prominent role in shaping the way we interact with and consume digital content in the years to come.
 The Rise of Monitors with Integrated Speakers
The Rise of Monitors with Integrated Speakers








 Introduction:
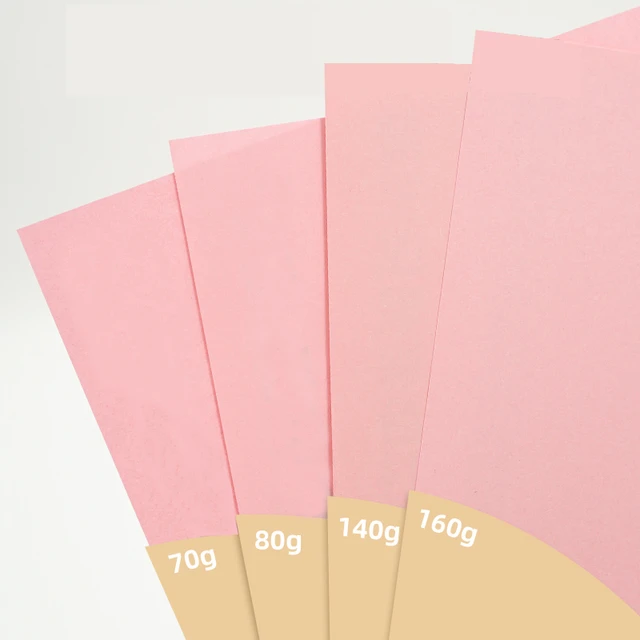
Introduction: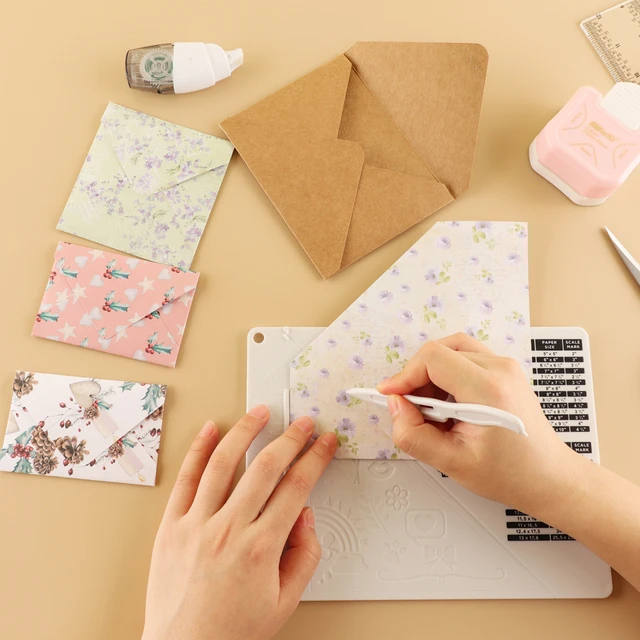 Paper Sizes and Weights in Printing
Paper Sizes and Weights in Printing Folding and Cutting the Paper
Folding and Cutting the Paper Benefits of Using Printed Paper for Envelope Making
Benefits of Using Printed Paper for Envelope Making Conclusion:
Conclusion:
 Introduction:
Introduction: Common Paper Weight Classifications
Common Paper Weight Classifications Selecting the Right Paper Weight
Selecting the Right Paper Weight Conclusion:
Conclusion: Introduction:
Introduction: Understanding Paper Sizes
Understanding Paper Sizes Choosing the Right Paper Size
Choosing the Right Paper Size Here are some key roles of standard printer paper in the office:
Here are some key roles of standard printer paper in the office: Conclusion:
Conclusion: Introduction-What is the size of printer paper:
Introduction-What is the size of printer paper: Letter and Legal Paper Sizes
Letter and Legal Paper Sizes Here are the key reasons why printing paper is essential in the workplace:
Here are the key reasons why printing paper is essential in the workplace: Here are some popular trends in printing paper:
Here are some popular trends in printing paper: Conclusion:
Conclusion: Introduction-normal printer paper size:
Introduction-normal printer paper size: Understanding Paper Sizes
Understanding Paper Sizes Choosing the Right Paper Size
Choosing the Right Paper Size Conclusion-normal printer paper size:
Conclusion-normal printer paper size: