Introduction to Network Gateways and Routers
Understanding gateway vs router is essential for anyone dealing with network infrastructure. A network gateway acts as a ‘bridge’ for communicating between different systems, often using diverse protocols. Meanwhile, a router is a device that forwards data packets between networks, ensuring that the information reaches its intended destination.
Both gateways and routers are integral in managing network traffic, yet they perform distinct functions. A gateway translates data formats and protocols so networks can communicate, while a router directs traffic efficiently using address information. Their roles, when combined, maintain the flow of data across the vast realm of interconnected networks.
In essence, think of a gateway as a translator enabling two people speaking different languages to understand each other, and a router as a guide that ensures you take the most efficient route to your destination. This guide begins by revealing their unique purposes and progresses towards their collaborative functions in network architecture. Recognizing their differences and when each is required will empower better network design and implementation.

Defining a Network Gateway
A network gateway acts as a communication link between different networks. By converting data formats and protocols, it allows systems to interact despite differences.
The Role of a Gateway in Network Communication
Gateways play a crucial role in network infrastructure by linking disparate networks. They translate communications so data can flow between networks with distinct protocols.
Types and Functions of Gateways
Gateways vary in form, from simple software applications to complex hardware devices. They serve functions such as protocol conversion and managing cross-network traffic.
Exploring Network Routers
Routers are crucial for network traffic management. They ensure data flows smoothly between different networks and connected devices. Routers direct data packets based on IP addresses. They analyze traffic, identify destinations, and use routing tables to guide packets efficiently.
How Routers Manage Data Traffic
Routers control data traffic by analyzing and directing data packets. They make use of routing tables to determine the best paths for traffic. These tables are key to efficient routing outcomes. By checking packet addresses, routers forward data along optimal network paths. This role is vital for network reliability and speed.
Different Types of Routers and Their Uses
Various routers serve distinct network needs. Examples include residential routers, enterprise routers, and edge routers. Residential routers connect home devices to the internet. Enterprise routers handle more traffic, offer high performance for businesses, and support complex networks. Edge routers manage traffic between different networks, often in Internet Service Provider (ISP) environments.

Comparing Gateways and Routers
Navigating the complexities of network infrastructure often leads to a critical question: gateway vs router – which do I need? While both devices are vital for data flow management across networks, understanding their similarities and differences is fundamental for optimal network performance.
Similarities in Network Traffic Management
Gateway vs router share some key functions in overseeing data traffic. Both sit at network layer three, directing data based on IP addresses. They use routing protocols to steer data paths and have security measures like firewalls.
- Both handle routing and packet forwarding.
- They function at network layer three of the OSI model.
- Routing protocols such as OSPF and BGP are common to both.
- Security measures like VPNs and firewalls are implemented by both.
- Routers and gateways can scale to support large networks.
- Integrated network cards are a feature of both, eliminating the need for separate cards.
In certain setups, routers can double as gateways. This dual role is evident when they move traffic both within and between networks.
Key Differences in Functionality and Application
Despite these similarities, gateways and routers have distinct roles. Gateways serve as the interlinking point between different networks, especially those with dissimilar protocols. They perform critical conversions ensuring that devices can communicate across these varied networks.
Routers, however, primarily manage the flow of data within and between similar networks. They determine the best pathways for data packets, focusing on efficient and speedy traffic delivery.
- Gateways bridge and translate between disparate networks.
- Routers focus on determining the most efficient data paths.
- Gateways handle protocol and format conversions.
- Routers maintain and consult routing tables for data direction.
To summarize, gateways are the multilingual translators ensuring networks ‘talk’ to each other, while routers are the traffic directors assuring that data ‘travels’ effectively. Picking the right device depends on the specific network needs and the type of data traffic encountered.
The Interplay Between Routers and Gateways
Navigating the realm of network infrastructure, we come across gateway vs router. Their interplay is critical for seamless data flow across various network environments. Let’s dive into when and why each device becomes imperative and how they sometimes overlap in functionality.
When Gateways Become Necessary in Networking
Gateways become vital when connecting disparate networks with different communication protocols. They serve as translators, ensuring that devices across these varied networks can understand each other and exchange data effectively. Whenever there’s a need to bridge distinct network systems, gateways are the go-to solution. They enable devices to ‘speak’ to one another, converting protocols and managing traffic flow.
For instance, integrating a legacy system with a modern VoIP network requires a gateway to translate between the incompatible protocols. Similarly, interconnecting an enterprise’s internal network with an external one, such as the Internet, often calls for a gateway to manage the data translation and ensure secure and coherent communication.
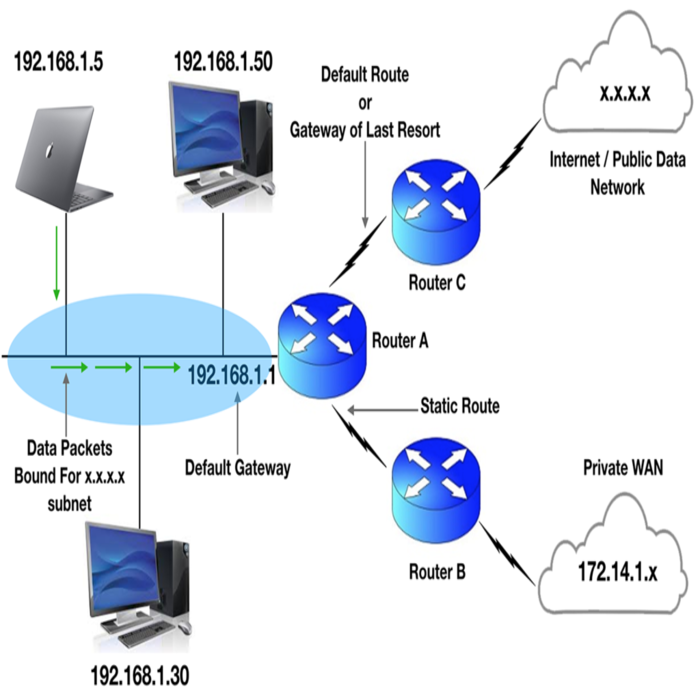
Scenarios Where Routers Serve as Gateways
While routers are typically tasked with directing traffic within and between similar networks, they sometimes take on the role of gateways. In home or small business environments, routers facilitate the connection to the broader Internet, acting as the default gateway for all local devices. In this dual capacity, routers not only manage local traffic but also serve as the entry and exit point for data moving in and out of the network.
Furthermore, in certain network designs, routers are configured to connect different subnets within a larger network. They enable devices on these subnets to communicate, smoothing out data transfer while still maintaining efficient routing. In cases where multiple networks with shared protocols need interaction, routers equipped with gateway capabilities prove to be both practical and cost-effective.
Understanding the nuanced roles of routers and gateways equips us with the knowledge to optimize network setups, enriching communication and enhancing the overall network performance.
Understanding Network Layer Protocols
Network layer protocols are crucial for data communication and network operations. These protocols determine how data packets are managed, routed, and transferred across a network. Routers and gateways both interact with these protocols, but in different ways.
How Routers and Gateways Handle Protocols
Routers mainly work with network layer protocols like IP to direct data packets to their destinations. They use protocol information to make routing decisions. Routers maintain routing tables based on these protocols to ensure efficient data passage. Gateways also interact with network layer protocols. However, their primary task is protocol conversion. This enables communication across networks with different protocols. This conversion process ensures data can seamlessly transit between these diverse networks.
The Impact of Protocols on Data Packet Processing
The role of protocols in processing data packets is immense. Network layer protocols set rules for how data is formatted, addressed, sent, and received. Routers use this protocol information to move packets along the best paths. They ensure packets reach the correct network destinations. Gateways ensure that the protocol differences do not impede data exchange. They translate protocol languages so that one network’s packets can be read and understood by another network.
Protocols govern data flow, influence router paths, and trigger gateway translations. Understanding these protocols and their functions within routers and gateways is essential for network efficiency and compatibility.
Configuration and Deployment
Properly configuring and deploying gateway vs router is vital for efficient network operation. This section offers insights into setting up these devices in different settings.
Setting Up Gateways in Various Environments
Configuring gateways largely depends on the network requirements. For example:
- In a corporate setup, gateways enable communication between the company’s network and external networks.
- For home use, a gateway may simply provide internet access to various devices.
While setting up, consider the following:
- Ensure the gateway supports the required protocols of both networks.
- Update the device firmware to the latest version for security.
- Configure the network settings, including IP addresses and DNS.
- Test connections and data flow to verify proper setup.
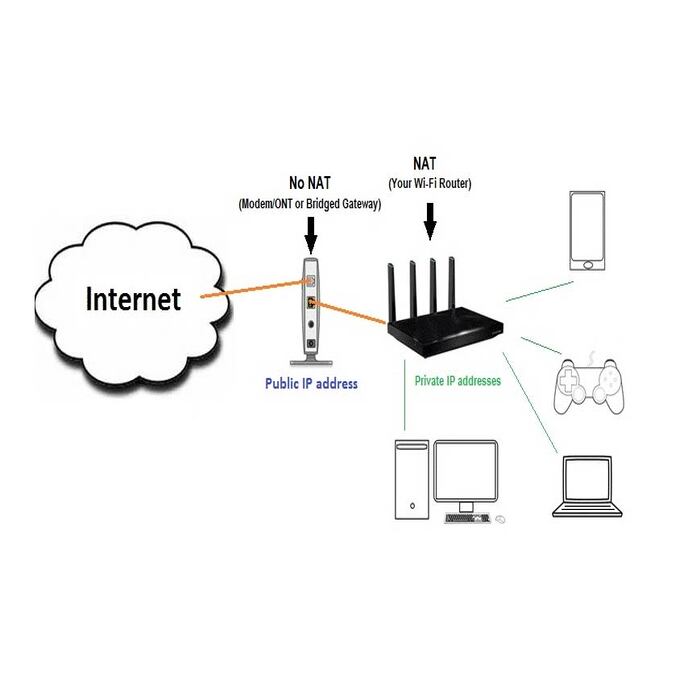
Routers: Installation and Network Integration
Routers direct internet traffic and connect devices. Key steps in router installation include:
- Connect the router to a power source and your modem.
- Set up the router’s network name (SSID) and password via its web interface or app.
- Adjust settings like DHCP, NAT, and QoS as needed for your network.
- Update the router’s firmware to protect against threats.
After installation, routers should integrate smoothly with your network, directing traffic and maintaining connection reliability. Regular checks and updates ensure routers remain effective over time.
Conclusion
Choosing the right networking device—be it a gateway or a router—depends on your specific needs. If your goal is to facilitate communication between different networks, especially those with varying protocols, a gateway is essential. It translates the communication protocols, allowing for seamless data exchange.
Conversely, for directing traffic within or between similar networks, a router is more appropriate. It reads data packets’ destination addresses and routes them through the most efficient paths, utilizing routing tables.
Choosing Between Gateway and Router for Your Network Setup
In deciding which device to use, consider the following points:
- If your network needs to connect with another network using different protocols, opt for a gateway.
- For traffic management and data packet routing within a single network or between similar networks, choose a router.
- Identify if the need is for data translation (gateway) or data direction (router).
Whether it’s a home setup or a corporate network, understanding the roles of these devices will ensure a reliable and efficient network configuration. Always consider the layout of your network, the devices you wish to connect, and what kind of data traffic you expect. With this in mind, you can make an informed decision to optimize your network’s performance.




